Wealth inequality in Germany has profound implications for financial planning, shaping the economic landscape and influencing individuals’ ability to achieve financial security. With a significant portion of the country’s wealth concentrated in the hands of a privileged few, access to resources and opportunities becomes increasingly skewed. This imbalance not only exacerbates disparities in income and asset ownership but also hampers the ability of individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds to plan for their financial futures effectively.
From limited access to essential financial services to challenges in saving for retirement and securing affordable housing, wealth inequality permeates every aspect of financial planning, posing formidable obstacles to socioeconomic mobility and perpetuating intergenerational disparities. Addressing this issue requires concerted efforts from policymakers, educators, and society to create a more equitable economic environment where all individuals can thrive financially.
Understanding Wealth Distribution in Germany
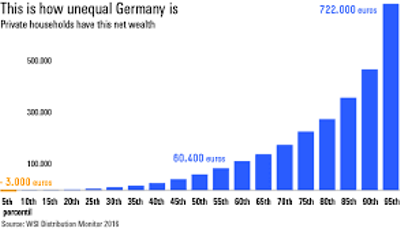
Despite Germany’s strong economic performance and robust social safety nets, wealth distribution remains skewed. Recent studies reveal that a small fraction of the population holds a disproportionately large share of the country’s wealth. The wealthiest 10% own over half of Germany’s net wealth, while the bottom 50% possess only a minimal share. This concentration of wealth has been exacerbated over time, raising concerns about its implications for social cohesion and economic stability.
Factors Contributing to Wealth Inequality
Several interconnected factors contribute to the persistence of wealth inequality in Germany:
Economic Policies:
The impact of economic policies, including tax regulations and financial incentives, often favors the affluent segments of society. For instance, tax breaks for capital gains and inheritance disproportionately benefit wealthy individuals, further widening the wealth gap.
Education and Skill Disparity:
Disparities in access to quality education and skill development opportunities perpetuate intergenerational wealth gaps. Children from affluent backgrounds have better access to educational resources, leading to higher earning potential in adulthood, while those from disadvantaged backgrounds face barriers to upward mobility.
Taxation System:
Germany’s progressive taxation system, while progressive compared to many other countries, still contains loopholes allowing the wealthy to minimize their tax burdens. Rich individuals often use tax avoidance strategies, such as offshore investments or corporate structures, reducing the tax revenue available for social welfare programs and public services.
Read More: German Capital Markets: Trends and Opportunities
Impact of Wealth Inequality on Financial Planning
The ramifications of wealth inequality extend beyond income disparities to various aspects of financial planning:
Limited Access to Resources:
Individuals with limited financial means face challenges accessing essential financial services like banking, credit, and insurance. This limited access restricts their ability to save, invest, and accumulate wealth over time, perpetuating the cycle of poverty.
Challenges in Retirement Planning:
Wealth inequality poses significant challenges for retirement planning, particularly for low-income earners. Limited savings and inadequate pension provisions often result in financial insecurity during retirement years, forcing many elderly individuals to rely on state benefits or family support.
Housing Affordability:
The widening wealth gap exacerbates housing affordability issues, particularly in urban areas. Rising property prices and rental costs outpace income growth for many, making homeownership unattainable for low and middle-income households. This housing insecurity further amplifies socioeconomic disparities and perpetuates intergenerational wealth gaps.
Strategies to Address Wealth Inequality
Addressing wealth inequality requires a comprehensive and multi-faceted approach:
Policy Interventions:
Implementing progressive tax reforms, closing tax loopholes, and increasing tax transparency can help redistribute wealth more equitably. Investing in social welfare programs, affordable housing initiatives, and job creation strategies can alleviate economic disparities and promote inclusive growth.
Education and Skill Development Initiatives:
Enhancing access to quality education and vocational training programs can empower individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds to improve their earning potential and socioeconomic status. Investing in lifelong learning opportunities and retraining initiatives can also mitigate the impact of technological disruptions on employment and income inequality.
Progressive Taxation Reforms:
Introducing higher marginal tax rates for top earners, imposing wealth taxes on high-net-worth individuals, and implementing inheritance tax reforms can generate additional revenue for social welfare programs and reduce wealth concentration. These progressive taxation measures can foster more significant economic equity and contribute to a more just society.
Case Studies of Successful Financial Planning Despite Inequality
While wealth inequality presents formidable challenges, there are instances of individuals and families successfully navigating the financial landscape:
Prudent Financial Management:
By adopting sound financial practices, such as budgeting, saving, and investing wisely, individuals can mitigate the impact of wealth inequality on their financial well-being. Strategic asset allocation and diversification strategies can help build resilience against economic uncertainties and market fluctuations.
Access to Specialized Resources:
Seeking guidance from financial advisors, wealth managers, and legal experts can provide individuals access to specialized resources and personalized wealth accumulation and preservation strategies. Despite prevailing inequality, economic tools and products like retirement accounts, insurance policies, and investment portfolios can optimize financial planning outcomes.
Read More: Risk Management Practices in German Financial Institutions
Conclusion
In conclusion, wealth inequality in Germany poses significant challenges to financial planning and societal cohesion. Addressing this complex issue requires concerted efforts from policymakers, educators, businesses, and civil society organizations. By implementing progressive policies, investing in human capital, and promoting inclusive economic growth, Germany can strive towards a future where wealth is more equitably distributed and financial security is accessible to all its citizens.
FAQs(Wealth Inequality in Germany: Impact on Financial Planning)
Is wealth inequality a significant issue in Germany?
Yes, wealth inequality is a pressing concern in Germany, with a small percentage of the population holding a disproportionate share of wealth.
How does wealth inequality affect retirement planning?
Wealth inequality can make retirement planning challenging for individuals with limited resources, leading to financial insecurity in old age.
What role do economic policies play in exacerbating wealth inequality?
Economic policies that favor the affluent, such as tax breaks and subsidies, contribute to widening the wealth gap in Germany.
Are there any successful strategies for addressing wealth inequality?
Yes, strategies such as progressive taxation, investments in education, and targeted welfare programs have shown promise in mitigating wealth inequality.
Can individuals overcome wealth inequality through financial planning?
While wealth inequality presents challenges, individuals can still achieve financial stability through prudent financial management and strategic investments.











